In April 2023, we saw a decline in our ability to generate capital gains and dividend revenue. Many investors will pay tax on their investments for the first time when both allowances are cut in half and then again in 2024.
In light of this, if you have not considered investing tax efficiently, you might want to consider seeing if you could benefit more now than ever from a tax-efficient account like a self-invested personal pension (SIPP) or stocks and shares ISA.
The value of tax savings and one’s eligibility to invest in an ISA or SIPP are dependent on individual circumstances, and tax laws are subject to change.
What is a Dividend?
When a limited company generates profits and then makes payments to its shareholders from them, they are called dividends. Only a profitable company can make such payments. Thus, the payout cannot exceed the profits the company generated in the previous and current financial years.
The money your company has after it pays all its tax liabilities and expenses is called profit. Tax liabilities of a limited company include corporation tax and VAT. While expenses are wages and the rent for the premises the company uses. After tax, if your company does not have enough profit to pay out a dividend, then it is illegal for it to do so. It cannot cover the amount of dividend payments. Please note that dividend payments are not like salaries, and do not classify as a business expense.
If your limited company accumulates profits over several years, it is called ‘retained profit’. Directors do not need to distribute profits to shareholders when the accounting year of the company ends. Rather, they can retain the profits of the business. It is possible to distribute these profits in the future.
Since it is a tax-efficient way to extract money from business, shareholders usually draw their earnings as dividends.
How to Issue a Dividend in the UK
It is mandatory to hold a meeting of your directors to issue a dividend. You must declare a dividend. For legal reasons, you must minute the meeting and keep a record of it. Your year-end approval documents include these records at the time your accounts are signed.
Moreover, it is important to have a copy of the profit & loss account along with the balance sheet. This way you can make sure that the payment is not more than the profits that are in the business bank account.
You must issue each dividend payment as a dividend voucher. Every individual that receives a dividend must also receive a copy of the voucher. For your accounting records, you also need to keep a copy. The voucher should contain essential information, including:
- Name of your company.
- Registration number of your company.
- Names of all shareholders that received dividends.
- Date of the dividend payment.
- Amount of dividend.
- Share class.
- Authorising officer’s signature.

How to Work Out Dividend Payments
The record of dividends takes place when they are set out for payment. To calculate the amounts of payment you use the percentage of company shares that each shareholder owns.
Suppose you have four shareholders who own an equal split of all shares. In this case, 25% of all dividend distribution is the amount each shareholder will receive. If your company has a retained profit of £8,000 then each of them will get £2,000 as a dividend payment. Nevertheless, there are certain exceptions.
It is important to note that if you do not record your dividends properly, then they may be seen as directors’ loan accounts. As a result, the company will end up paying more taxes.
How Much is it Possible to take in Dividends?
There is a common misconception that you can pay out dividends from any cash in the business bank account. That is not always the case. A limited company can distribute all its accumulated realised profits minus its accumulated realised losses.
Realistically, you must factor in unrealised losses. Therefore, if ensuing losses eliminate your earnings, then you cannot pay out dividends on accounts showing profits. If an unlawful dividend payment takes place, then directors are liable personally. However, to pay yourself dividends you should use the best structure:
Shareholders need to repay a dividend distribution if they know its illegal nature at the time of payment. The Company Act states this liability.
It is important to review the Memorandum of Articles of the company. This can include statements regarding restrictions on dividends in specific situations. Furthermore, different types and classes of shares may exist. They can affect entitlement to voting rights and dividends. The statement of capital covers the details of the shares and rights of the company to them.
Is it Beneficial to Receive Dividends?
Yes, it is indeed beneficial for you to receive dividends. Especially since on earning up to £50,270, the dividend tax rate is 8.75%. Most UK residents pay 20% income tax on their salaries along with a 10% National Insurance Contribution. Therefore, they must pay 30% on all earnings that exceed the annual allowances.
Nevertheless, it is not always a good idea to receive a dividend. You should contact your accountant to find out the most tax-efficient methods of dividend payments. Your financial situation and your company’s financial circumstances determine the best option for you.
What are the Timings for Dividends?
When there is enough cash available in the business after agreeing on the year-end figures, dividend payments usually take place. Final dividends are how you refer to them. Although, if you want you can pay yourself dividends at any time. That is if there is sufficient money available.
If you make payments any time during the year, then they are called interim dividends. Hence, there is no limitation on how many dividends your company can issue during the year. This is according to the company’s retained profit and financial performance.
Every time you declare dividends, you must issue only one dividend for each shareholder. Consequently, by issuing more dividends you increase the amount of admin and paperwork for completion.
There are personal tax implications for how and when you make a dividend payment. These depend on your level of personal income and when the introduction of certain tax changes takes place. It is ideal to reach out for professional advice when extracting profit. This way you know the possible estimated tax liabilities.
How Much Dividend is Tax Free?
Fortunately, there is a certain amount you can receive in dividends that is tax-free. This is called dividend tax allowance. You do not owe tax until you exceed this amount.
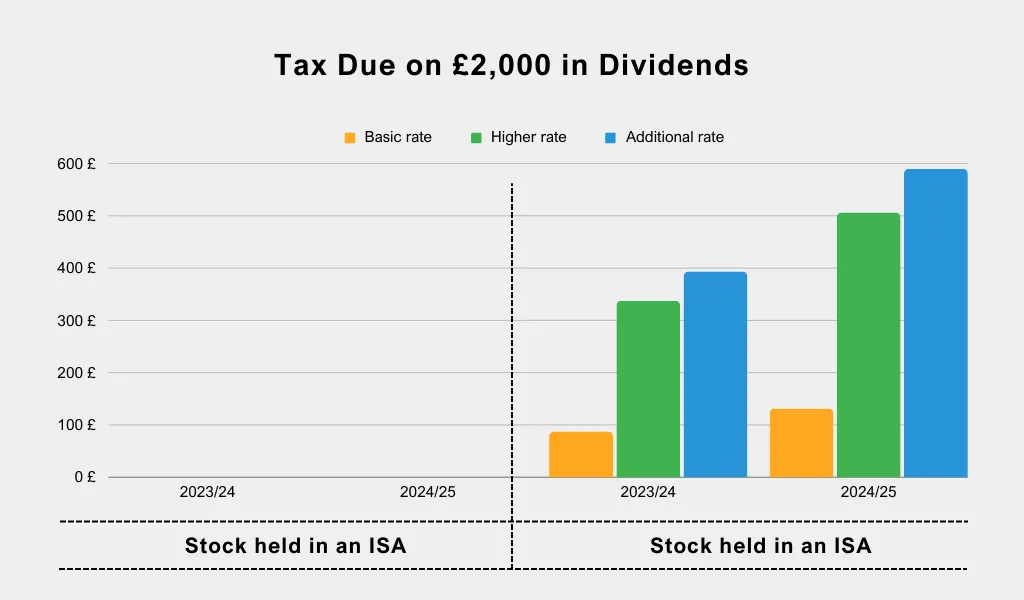
For the 2023/24 tax year, the amount cut down from £2,000 to £1,000.
This amount will be cut down to £500 in the tax year 2024/25.
Undoubtedly, this is a drastic decrease. The dividend allowance was £5,000 only six years ago.
Please note that when you issue dividend payments through ISAs, they are tax-free.
What are the Dividend Tax Rates?
Once you exceed the dividend allowance, you owe tax. The amount of tax you must pay is according to your income tax band.
You must add your general income to your dividend income to determine your tax band. Your general income is your regular salary. The table below shows the dividend tax rates for the current tax year:
| Band | Taxable Income | Tax Rate | Dividend Tax Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Personal Allowance | Anything up to £12,570 | 0% | 0% |
| Basic | £12,571 to £50,270 | 20% | 8.75% |
| Higher | £50,271 to £125,140 | 40% | 33.75% |
| Additional | More than £125,140 | 45% | 39.35% |
Example
You are going to receive £10,000 as a dividend payment, and that is your entire income for the 2024/25 tax year.
Your annual dividend allowance covers the first £500.
The remaining £9,500 falls within the threshold of your personal allowance. This is £12,570 for the relevant tax year.
Since your allowances cover the entire amount, none of your income is taxable. Therefore, you get to keep the entire dividend payment of £10,000.
How to Pay Dividend Tax
How much you earn as dividend income determines your method of payment of tax on dividends. If you are a self-employed individual, then you must use your Self-Assessment tax return.
- You need to inform HMRC through their helpline if you earn up to £10,000. Or you can request them to change your tax code.
- In case you earn more than £10,000, then you must declare it on your Self-Assessment tax return.
How to Reduce the Amount of Tax You Owe on Dividends
The need to use tax-efficient pensions and ISA accounts is now greater than ever because of the reduction in the dividend allowance. Both income and profits are not subject to tax. You can build up a substantial portfolio of investments that are safe from tax by using as much of the ISA allowance as possible. Not only this, but you can remove the administration of reporting to HMRC and filing tax returns.
For those who are married or in a civil partnership, it is possible to split income-producing assets. They can do so by transferring them to their partner who has a lower income and tax liability. Also, they can hold these assets in joint names.
Furthermore, you can factor in the arrangement of your asset types. Investing your ISA allowances mostly in dividend-producing securities rather than cash, for example, may make sense. Since the “starter rate” for cash interest can reach £5,000, some people’s personal savings allowance applied to cash interest is much more than the dividend allowance, and cash return is frequently less than dividend return. It will, however, depend on your tax status, the type of assets you possess, and the amount of interest you receive on cash.
Thus, if you have earned income from a job or self-employment and would like to lower your overall tax liability, you might want to think about making more pension payments.
Your earned income may decrease as a result, putting less of it in the higher tax brackets. Please be aware that Scotland’s income tax rates and bands differ from the rest of the UK.
Conclusion
To summarise, you should understand how dividends work in a limited company. There is a procedure for issuing dividends which you must follow. Not only this but make sure no dividend payments are illegal for your company. Your business must have sufficient profits available to make dividend payments to its shareholders. There is a certain amount of dividend that you receive before you start paying tax. This is called your dividend allowance. For the 2024/25 tax year, there is a reduction in this allowance. Therefore, it is important to know tax-efficient ways of investing such as ISAs. Remember, it is best to reach out for expert advice.








