As a property owner, it is necessary to understand how capital gains tax works. If you decide to sell your property, you may end up paying CGT on the profit you make from it. However, that is not always the case. There are exemptions to capital gains tax. Your primary residence can qualify for relief. This guide will answer the question: are primary residence capital gains subject to tax?
First, let us discuss the definition of capital gains tax and how it works. Then, we can discuss private residence relief.
What is Capital Gains Tax?
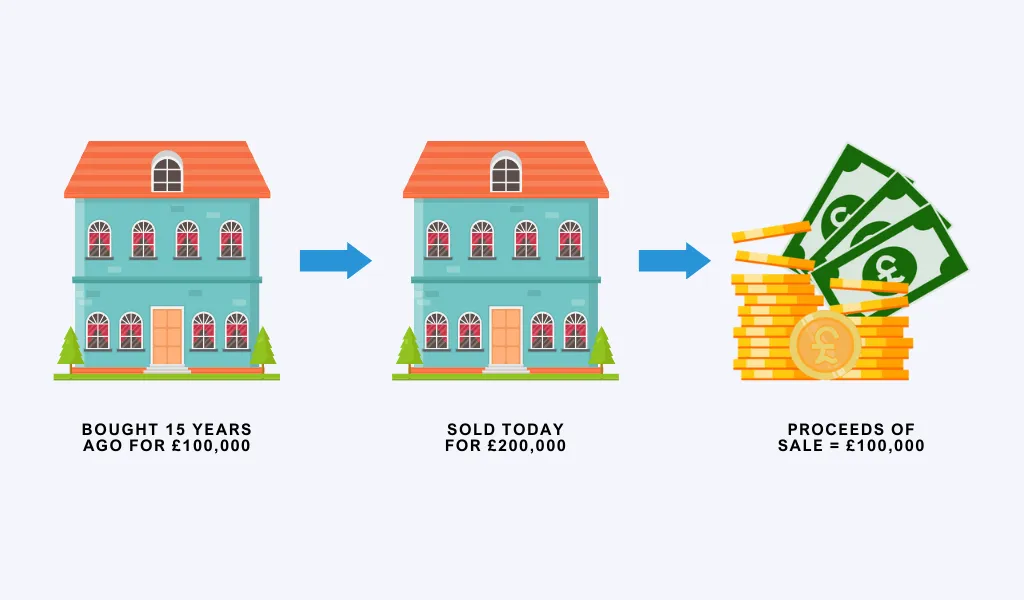
A tax charge that applies to the gain you make from selling your asset is called Capital Gains Tax (CGT). The calculation of CGT takes places on the profit you make. Which is the increase in the value of the sale price in comparison to the purchase price. This applies to assets that you hold for more than one year.
Usually, CGT applies to:
- Shares.
- Investment funds.
- Sale of a business.
- Second homes.
- Valuables, including jewellery, art, and antiques.
- Inherited properties.
- Assets that you transfer at below their market value.
These assets are currently subject to capital gains tax at rates that differ from income tax rates. This is because investing in such assets is viewed as a risk, whether it be investment-related or entrepreneurial, and so, the potential payoff for taking on further risk is higher.
How Does CGT Work?
There is no automatic deduction by HMRC in the case of CGT, unlike income tax. This means that you must report it. Since various fiscal triggers exist, you should know what requires reporting. If you fail to provide accurate reports to HMRC, you will end up facing a fine that is more than your tax bill. Therefore, notifying HMRC is crucial.
What are the Capital Gains Tax Rates 2023/2024?
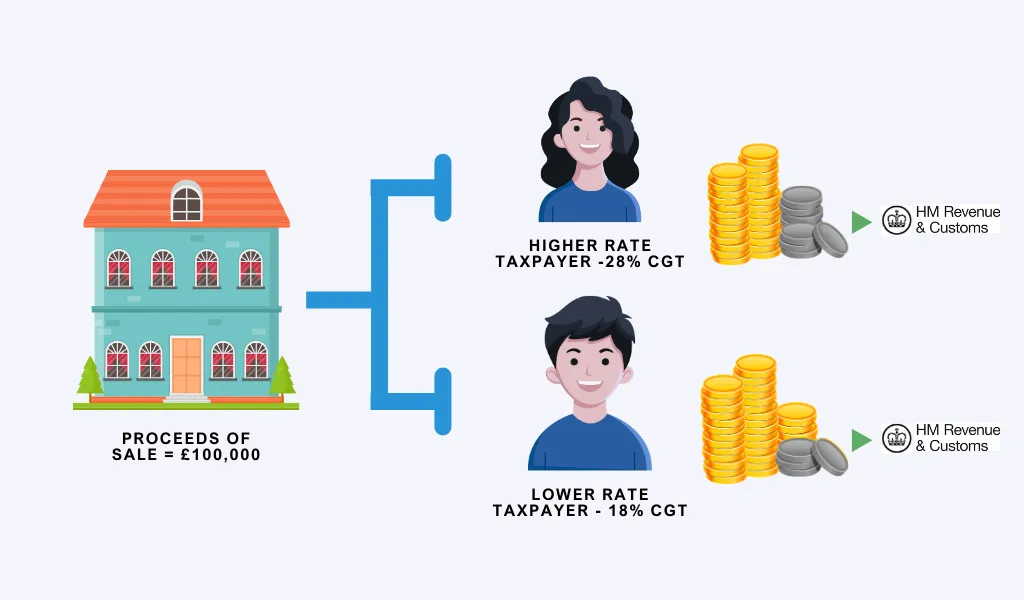
It is important to note that CGT rates differ from income tax rates. Two broad brackets exist with CGT. One is of basic rate taxpayers and the other of higher/additional rate taxpayers. For basic rate taxpayers, the CGT rate is 18% on residential property and 10% on other assets. Whereas for higher rate taxpayers, the CGT rate is 28% on residential property and 20% on other assets.
| Type of Asset | Basic Rate Taxpayer | Higher/Additional Rate Taxpayer |
|---|---|---|
| Residential property | 18% | 28% |
| Shares (not held within an ISA or PEP) | 10% | 20% |
| Other | 10% | 20% |
What is Capital Gains Tax Allowance?
You do not need to worry when doing your tax return as you have a capital gains tax allowance.
Now, how much is this allowance? Well, for individuals, it is £6,000 in the 2023/2024 tax year. Whereas for trusts, it is £3,000. This means that you can make a profit of up to £6,000 before CGT begins to apply. A reduction is going to place in April 2024, as it will go down from £6,000 to £3,000 for individuals.
For those who have joint ownership of a taxable asset, the allowance is double the amount. Which means up to £12,000 of gains is exempt from CGT. An example of joint ownership of a taxable asset is a second home.
If you transfer assets to your partner, and make a gain afterwards, the rules change. The CGT that you owe depends on the total time of your ownership of the assets together instead of the date of transference. Therefore, what are the tax implications of primary residence capital gains?
When you sell your primary residence, you do not need to pay CGT. However, it applies when you sell your second home. Also, it applies when you let out your primary residence or use it for business purposes. Depending on your tax bracket, the CGT rate is 18% or 28%.
When it comes to stock and shares, the CGT rate depends on your tax bracket as well. The rates are different in this case. They are 10% or 20%.
Does Tax Apply to Primary Residence Capital Gains?
When you sell a property and gain profit, you may need to pay CGT. Owing CGT depends on whether the property is your primary residence or second home. Your principal residence is exempt from CGT as private residence relief applies to it. If the property you are selling is your second home or any other real estate, it is subject to CGT. It is important to understand how CGT works when it comes to primary residence capital gains.
What Qualifies as a Primary Residence for CGT Purposes in the UK?
If all the following apply, then your property is considered as your primary residence for the purposes of CGT:
- For the duration of ownership of the property, you lived there.
- The property you are selling is your only property.
- You did not use any part of your home for business purposes only.
- The total size is less than 5,000 square metres. This includes all the buildings and all the grounds.
- The sole purpose of purchasing the property was not to make a gain.
Once you meet all these criteria, you will receive private residence relief automatically. You will not have to pay any tax. However, if you cannot meet one or more of these conditions, you may end up paying partial CGT.
How Does Private Residence Relief Work?
So how does PRR work? Well, it applies whenever you sell a “dwelling house” or dispose of it. The dwelling house must be your only or principal residence. Now, the question arises what constitutes a “dwelling house.” Legislation does not define it. Nevertheless, you can refer to a body of case law built up over a long time.
Typically, the entire building in which you live is a dwelling house. Additionally, this can include any relevant buildings that are adjoined to the main building. For example, a garage, outside study, or a workshop that is a part of the overall household.
Along with the building, the garden area will also qualify for PRR. That is, if it is within a permitted area. An area that is less than 5,000 square metres is a permitted area. Nevertheless, an area larger than this can qualify if HMRC permits it. The condition is that it is necessary for the ‘reasonable enjoyment’ of the property. Now, you know CGT does not apply to primary residence capital gains. If you utilise any part of your home for business, then that part does not qualify for relief upon sale. Please note that if you use a room for occasional remote working, then it does not count for business purposes.
When You Sell Your Family Home
If you decide to sell your family home, then Capital Gains Tax will not apply. This is true for most instances. On the other hand, this situation is more complex if you use part of your property for business purposes. Or even if you own more than one home.
When Do You Qualify for Partial Relief?
Even if you do not meet all the criteria to qualify for full relief, you may still get partial relief. How do you figure out if you can receive partial relief? Well, you must fill out the necessary CGT tax return summary pages. Then, HMRC will review your form. They will inform you whether you qualify for at least partial Private Residence Relief. Therefore, some CGT can apply to primary residence capital gains.
What are the Criteria for Qualification for Private Residence Relief?
To qualify for PRR, you must be a resident for tax purposes in the same country as the property for the tax year. So, if you are selling the property, you must meet this requirement as of April 2015.
Capital Gains Tax for Non-Residents on UK Residential Property
If you are a non-UK resident who is disposing of their residential property, then you will not get PRR. To qualify, you should have spent a minimum of 90 midnights on the property.
Other Considerations for Private Residence Relief
Dwelling House: Anything ranging from a house to a flat to a houseboat or even a fixed caravan. If it is your home.
Only/Main Residence: Throughout the time you owned the property, it remains your only or primary residence.
Period of Ownership: This is the length of period you owned the home from the point of purchase to the completion of a sale. This provides you with the basis to calculate Private Resident Relief. It is important to understand how to qualify for exemption for primary residence capital gains.
Job-related Accommodation: You and your spouse live in a home because it is part of your job requirement. Furthermore, your primary residence is somewhere else. These factors determine Private Resident Relief.
Garden or Grounds: For garden or grounds, there is no statutory definition. Grounds usually mean an area that is larger than a garden. You can find guidance through HMRC on the following definitions:
- Garden: it is a piece of ground, which partly has grass. They adjoin it to a private home where you grow vegetables, fruits, or flowers. Additionally, it is a recreational place.
- Grounds: it is attached to a dwelling house and is an enclosed land. It can also surround the dwelling house. It serves the purpose of recreation or ornament.
- Any land that is not a garden or grounds does not qualify for relief. This applies even if the total size of land is within the permitted area.
Is it Possible to Claim Both Private Residence Relief and Letting Relief?
The short answer is yes, you can claim both Private Residence Relief and Relief. Although, it is only under certain circumstances.
Suppose you let out part of your property. Then, you need to figure out what part of your home you lived in. This is because you will get PRR on this specific proportion of your gain.
For example, you rent out a bedroom, which is 10% of your home. In this scenario, when you sell this property, you make a gain of £60,000. Let us just suppose. Since 10% of your property was on rent, you will get PRR on 90% of the gain. Furthermore, you can claim Letting Relief on the remaining 10%. Therefore, it is crucial to know how tax works when it comes to primary residence capital gains.
Thus, you can claim both and avoid paying Capital Gains Tax altogether.
Conclusion
To summarise, if you are selling a property that is your principal residence, it is not subject to CGT. In case it is your second home or any other property, then you need to pay capital gains tax. Your principal residence can qualify for private residence relief, thereby making it exempt from CGT. Please make sure your property meets the criteria for PRR. Even if you cannot qualify for full relief, you can be eligible for partial relief. It is crucial to notify HMRC regarding any capital gains you have in the relevant tax year. Failure to do so can have severe consequences such a hefty fines and penalties.








